8.20.2008
20 Jobs That Pay £20 Per Hour
Paul MacKenzie-Cummins for CareerBuilder.co.uk.
Many of us have taken a part-time job that paid £5 or so an hour whilst still at school or college, and probably never gave any thought as to how much this worked out to be on an annual basis. But according to a recent survey by AllTheTopBananas.com, the average salary in the UK is currently £20 per hour -- the equivalent of £31,969 a year.
Here is a list of jobs across various industries where you can earn between £20 and £25 per hour with each job role currently in demand and predicted to experience future job growth over the coming years.
1. Business Analyst (IT)
Average salary: £34,000-36,000
Job description: Identifies business or customer requirements from an IT perspective, develops and implements programmes to fulfil project requirements.
Entry requirements: Degree in a computing and/or business related discipline.
2. Chartered Accountant
Average earnings: £31,749 per annum
Job description: Analyses financial information and prepares financial reports to determine or maintain record of assets, liabilities, profit and loss, tax liability, or other financial activities within an organization.
Entry requirements: Degree -- preferably in business, economics, mathematics or law-related followed by completing the Chartered Institute of Taxation's Chartered Tax Account exams.
3. Solicitor
Average earnings: £34,045 per annum
Job description: Represents clients in criminal, civil litigation and other legal proceedings. Draws up legal documents and advises clients on legal transactions.
Entry requirements: Degree.
4. Marketing Manager
Average salary: £36,497
Job description: Plan and direct advertising and marketing campaigns to increase the sales of a product or service.
Entry requirements: Degree -- preferably in a business or marketing discipline, followed by the Chartered Institute of Marketing post graduate professional qualifications.
5. Public Relations Manager
Average salary: £33,768
Job description: Responsible for managing, developing and raising the profile and reputation of an organisation or individual to stakeholders or the general public.
Entry requirements: Degree is preferred but not essential. Excellent written and verbal communication skills are a pre-requisite and the ability to respond positively in a crisis.
6. Sales Manager
Average salary: £33,593
Job description: Plans and implements strategies to maximise the sales of a product or service. Ensures that targets are met on time and within budget.
Entry requirements: Promotion to manager level typically follows time spent on the shop floor as a telephone or field sales person. However, some organisations offer fast-track promotion for graduates.
7. Associate College Lecturers
Average salary: £33,000-35,000
Job description: Employed on a freelance basis, lecturers can be hired by more than one university or college for their expertise in a particular field.
Entry requirements: Most Associates are degree holders, however, many are hired for their extensive experience and working knowledge within a given subject area.
8. Architectural Assistant
Average salary: £33,000
Job description: Helps with the preparation of planning drawings for the senior architect.
Entry requirements: Previous exposure to planning applications and have a good knowledge of the UK Building Regulations, Microstation literate and ideally have freehand and knowledge of the Sketch Up programme.
9. Web Developer
Average salary: £30,000-33,000
Job description: Design, build and implement software programmes to be used via the internet.
Entry requirements: Experience of HTML, DHTML and CSS, and also of writing web-based user interfaces for database systems such as Microsoft SQL Server and IIS
10. Quantity Surveyor
Average salary: £34,000-35,000
Job description: Manages all costs relating to building projects with the aim of maximise the value of a property whilst ensuring that the property meets statutory building regulations.
Entry requirements: HND/HNC or a degree in a construction or engineering related subject will enhance your chances.
11. Tax Advisor
Average salary: £33,000-38,000
Job description: Responsible for preparing tax returns for both individuals and partnerships and advisory to include all aspects of tax planning to minimise income tax and capital gains tax liabilities.
Entry requirements: Degree in a finance-related discipline along with being ATT qualified and keen to study towards the CTA.
12. AutoCAD Technician
Average salary: £34,400
Job description: Responsible for the production of high quality drawings and details for all types of building structures projects
Entry requirements: HND in addition to 3 or more years of experience.
13. Senior Auditor
Average salary: £30-35,000
Job description: Assesses and reports on the potential risk factors affecting a business.
Entry requirements: Degree qualified, an understanding of FSA regulation coupled with ACA or ACCA professional qualifications.
14. Procurement Manager
Average salary: £32-35,000
Job description: Ensures the best value in the provision of goods and services through the development of strategic procurement policies and the effective management of a co-ordinated purchasing and supply service.
Entry requirements: Relevant business or CIPS qualification.
15. Management Accountant
Average salary: £30-35
Job description: Provides an effective cost and management accounting and information service to ensure that accurate and timely accounting information is provided.
Entry requirements: Graduate calibre plus professional accountancy qualification such as ACCA or CIMA.
16. Surveyor
Average salary: £30,000-35,000
Job description: Responsible for the financial accounting and project managements of a development from start to finish, procurement of materials and labour, valuations, and ensuring that the project is completed on time and within budget.
Entry requirements: Typically a minimum of three years of experience and proven management expertise.
17. Learning and Development Manager
Average salary: £30,000-35,000
Job description: Responsible for developing staff into potential managers through skills and knowledge training.
Entry requirements: Graduate calibre, preferably CIPD qualified.
18. Health and Safety Advisor
Average salary: £33,000-35,000
Job description: Advises the company in all matters relating to Health and Safety, Quality and Environmental issues and legislation.
Entry requirements: Experience of auditing to comply with British Standards (BS) plus Heath and Safety qualifications up to Diploma level with practical experience working across a whole range of disciplines.
19. Marketing Finance Analyst
Average salary: £33,000-38,000
Job description: Provides timely and accurate management information that will enable senior management to develop and execute effective plans and make informed business decisions.
Entry requirements: Degree coupled with being at least part-qualified in CIMA or ACCA.
20. Human Resources Manager
Average salary: £33,000-36,000
Job description: Responsible for an organisation's candidate attraction and retention procedures, the implementation and adherence of employment legislation.
Entry requirements: Usually at least three years of experience along with relevant CIPD qualifications.
SOURCE: CareerBuilder.co.uk.
8.06.2008
6.16.2008
The Sterling fall for the Euro

 The pound is registering all-time lows against the euro (although admittedly the price history here only goes back to 1999).
The pound is registering all-time lows against the euro (although admittedly the price history here only goes back to 1999).It wasn't so long ago all the talk was about exploiting the strong pound with a Christmas shopping spree in New York. Back in November, sterling touched a high of $2.11, now it is 7.5% lower. The pound has also fallen against the euro, down 7% from November. The scale and speed of sterling's decline against European currencies is not quite on a par with the pound's eviction from the ERM in September 1992. In that instance, sterling plummeted from just below DM2.80 to below DM2.20 in a comparatively short space of time. The equivalent fall in the pound since January 2007 has been from around DM3.00 to DM2.40.
The scale of sterling's fall so far is not yet comparable, but the reasons behind it are familiar. A deteriorating economic outlook which can only be addressed through interest rate cuts, because the Government has reached its overdraft limit. A perception of poor economic management has grown since the credit squeeze hit the world last August. And capital inflows from companies buying UK assets have slowed sharply.
Britain is more vulnerable to a sharp downturn than other major economies. London is the international hub of world finance. The UK economy is more dependent on investment banking and related high-value financial and business services than almost anywhere else. Banking profits have been hammered by the sub-prime debacle and this will be felt in Britain's most profitable economic activity. Meanwhile, the downturn in the fortunes of the financial sector will have an adverse impact on property prices in the capital, which in turn will ripple out to nearby regions.
Aside from the financial sector, the other fast growing area over the last decade has been public sector employment. But because the money already has been spent in the years of plenty, there's nothing left in the public kitty. Public employment has stopped growing and real spending power for government workers will probably be squeezed substantially this year.
This lack of prudence has been in evidence since 2001. But recently there have been mounting concerns about the Government's ineptitude. Its unnecessary prevarication over Northern Rock is already well documented. What concerns me is the Prime Minister's control freakery contaminating the Bank of England.
One of Gordon Brown's two most enduring achievements as Chancellor was the decision to give the Bank of England formal operational independence in setting interest rates, the other was keeping out of the euro. But ahead of the Bank's January monetary policy meeting, the Prime Minister and the Chancellor both came close to openly calling on the Bank of England to cut interest rates. Moreover, in Parliament Gordon Brown ignored David Cameron's invitation to announce whether he was going to offer Mervyn King a second term as Governor of the Bank of England. King's five-year period in office expires in the summer.(Article continues below)Advertisement
This unwise interference and the less than wholesome support for the Governor was picked up by the markets. Had the Bank cut rates this month, as it was under intense pressure to do, it would have been interpreted as a clear 'political' move intended to keep Mervyn King in his job. All of a sudden the Bank of England's independence is seen as somehow 'conditional'. No wonder the pound is on the ropes.Ironically, the political interference back-fired. The Bank of England Monetary Policy Committee was well aware of the dangers of cutting rates in response to political pressure, and chose not to. Who knows, they may have been more inclined to agree to a cut if the Government had kept quiet. Whatever events complicate the monthly decisions, one thing is clear: UK interest rates are headed lower.
High interest rates are the principal means of support for the pound. UK official rates are currently the highest in the developed world. The official Bank of England repo rate stands at 5.5%, compared with euro rates at 4.0%, US Fed funds at 3.5% and Japanese overnight call rates at 0.5%. But in six months time, the differential between sterling interest rates and those of other leading currencies will narrow as concerns about the UK's financial industry and the housing market mount.
Sterling is also overvalued on what economists call 'purchasing power parity' grounds. If the prevailing exchange rate is £1=$2, then if $2 buys far more in the US than £1 buys in the UK, then you can say that the pound is overvalued against the dollar. At the current exchange rate of £1=$1.95 this is certainly the case.
In 1986 the Economist popularised this notion of varying purchasing power between countries by introducing a Big Mac index. It's a light-hearted guide to determine how far currencies are from fair value, i.e. when a Big Mac costs the same in both countries in dollar terms. On average a Big Mac costs $3.41 in the US and £1.99 or $3.90 in the UK implying that the pound is still overvalued by 14%.
And history maintains that the pound is on the high side against the dollar. Since 1985, when the pound reached a record low (close to parity), the average dollar exchange rate has been $1.65. When the pound is overvalued it has a strong tendency to slide quite precipitously. It seems that traders are regarding a bet against the pound this year in the same vein as they regarded a bet against the dollar last year.
This is not all bad news though. I have long argued that politicians should not regard exchange rates as a symbol of national virility. Rather it is a very useful adjustment tool. Consider the predicament of the UK economy. Consumer spending and the financial services industry are heading for a phase of retrenchment; the Government is up to its borrowing limit, so the only outlet available for expansion is exports. A depreciation of the pound will do no harm in this respect, by making British exports more price competitive.
The downside is that a fall in the pound will push up the prices of imports. The big unknown is whether this will feed through into generalised inflation. It didn't happen after the pound's sharp decline in 1992. But then the UK economy had plenty of spare capacity and commodity prices were not the inflation threat they are now. It is hardly surprising that the Prime Minister is calling public sector workers to accept tight three year pay deals. If there is a pick-up in industrial strife it will be another reason to sell the pound.
By Brian Durrant for The Daily Reckoning
Should Britain now join the euro? 06-06-2008
How to profit from currency movements 04-04-2008
The dollar looks fragile - but sterling's far worse 17-01-2008
Can the sickly dollar ever recover? 16-06-2008
Should Britain dump the pound for the euro? 02-06-2008
Most Popular Articles
Why we shouldn't listen to City analysts
Why it's still not safe to go back in the water
What could be worse than the credit crunch? We’re about to find out
How mortgage figures mean dark times for the economy
Why it pays to hang on to gold
6.10.2008
Desperate Households - USA
June 2008
This year, millions of homes in the US will be repossessed. Wall Street was aware of the risks involved with sub-prime lending but chose to ignore them. No ethics, just money- here is a story of greed and recklessness.
In California, the sub prime crisis has hit homeowners full on. Repossessions have become routine and the foreclosure rate is still accelerating. Neat façades and tidy gardens can't prevent houses being sold for almost half of what they cost a year ago. Pressed for time and money, owners are torn out of their homes: 'It's like leaving your children' says Rob. He is hoping the bank will accept a quick sale and forgive the loss, but this is unlikely. Most are made to wait until they default on repayment, which wrecks their credit record. Former bankers reveal how low interest rates were meant to boost the economy. Banks looked for ways to make profit despite low rates and chased high-risk mortgages that would pay 8 or 9%, ignoring the consequences for borrowers if prices fell and interest rates rose again: 'There's no perception of the guy in some tiny little house in Detroit or in Philadelphia or in Stockton who basically might be losing their home.' Now that the system has failed, banks are less ready to lend money and this impacts on the entire economy. Families lose their homes, businesses fail...Wall Street gambled and the world has to pay.
L'immobilier fait des rabais sur Internet
 Acheter une maison ou un appartement sur internet, comme une chemise ou une paire de basket ? Loin d’être loufoque, cette possibilité est aujourd’hui une réalité.
Acheter une maison ou un appartement sur internet, comme une chemise ou une paire de basket ? Loin d’être loufoque, cette possibilité est aujourd’hui une réalité.Le site vente-privee.com propose ainsi, depuis lundi matin, en partenariat avec Kaufman &Broad, des biens en cours de construction dans toute la France. Sur la seule région Languedoc-Roussillon, sont mis en vente des appartements situés à Montpellier quartier Ovalie, Sète, Béziers et Perpignan.
La ristourne proposée sur le site reste raisonnable : autour de 5 %. Résultat : les internautes n’ont pas pris d’assaut ces appartements allant du deux au cinq pièces. Sur quinze biens mis à la vente seulement deux ont, sur simples plan et descriptif, trouvé preneur.
Une démarche analogue est menée à partir du 15 juin par le site avendrealouer.fr. Cette vente immobilière"flash" portera sur un volume de 100 logements neufs. Seule Montpellier est concernée dans la région. L’occasion pour les promoteurs immobiliers de relancer le marché auprès d’une clientèle en mal de pouvoir d’achat ?
5.31.2008
Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu , fl. c.500-320. BC, name used by the unknown Chinese authors of the sophisticated treatise on philosophy, logistics, espionage , and strategy and tactics known as The Art of War. It includes many commentaries by later Chinese philosophers.
Strategic Creativity
One example of creativity was that of Wheaties. During Superbowl XXXI in 1997 the Wheaties marketing team carried two boxes of Wheaties to the game; one representing the New England Patriots winning and the other the Green Bay Packers being victorious. As the game progressed, it became clear that the Green Bay Packers would beat the Patriots. With this in mind the Wheaties team went up to the broadcast booth, taking their box with Packer star quarterback Brett Favre's picture on it. The announcers, thinking it would be a great prop, took the box and showed it to the huge worldwide audience. By doing so they gave Wheaties millions of dollars of free advertising.
The major pharmaceutical company Johnson & Johnson has also displayed great creativity in marketing. Knowing that most people would not be drawn to their web site to learn about their medicines on a regular basis, J&J decided that perhaps events could help them create awareness for their products. With this thinking J&J runs banner ads for their headache reliever on e-broker sites whenever the markets drop significantly. Thus they reach consumers when those people are most interested in their products.
Consultants often point to the Gillette razor business model as an example of creativity. What most people don't know is how long ago that business model was developed and what the catalyst was behind it. All the way back in 1895 King Camp Gillette (yes, that was his real name) took his inspiration from a former employee who had made millions selling disposable bottle-tops. Using the idea that disposable razor heads, like disposable bottle-tops, were something that would need constant replacement, Gillette received a patent for his invention in 1901 and had sold 12 million blades by 1903. That same business model still works a century later.
Creativity is not something that belongs only to a few people who are born with it. John Kao, a well-known author of books on creativity (such as "Jamming") supports this view, stating, "Creativity must go beyond generation of new ideas; it must become an ongoing process." Roger von Oech, author of "A Whack on the Side of the Head" and many other books on creativity provides many exercises one can do foster it. Examples include being illogical, breaking the rules, and dealing with ambiguity. With these and other exercises one can be more creative and thus be more competitive.
As Sun Tzu said, "The flavors are only five in number but their blends are so various one cannot taste them all."
Turning Strengths Into Weaknesses
A key tenet of Sun Tzu's strategic philosophy is to attack the opposing side's weaknesses. "Now an army may be likened to water, for just as flowing water avoid the heights and hastens to the lowlands, so an army avoids strength and strikes weakness."
However, sometimes competitors seem invincible and few weaknesses are discernible. So another approach is to find ways to turn their strengths into weaknesses. For example, Coca-Cola's strength in the soft drink market was that it was the classic cola. With its long history as the favorite American drink, supported by decades of advertising, its position seemed unassailable. So Pepsi needed to find an approach that would work. It did so by turning Coke's strength into a weakness by coming out with the "Pepsi Generation" theme. This approach positioned Pepsi as the drink for the next generation of cola-drinkers, the youth market. It also positioned Coke as the drink for the older (and by implication, the old-fashioned) generation. With America's love affair with everything young Pepsi turned Coke's reputation as America's traditional drink from a strength to a weakness.
– Entrepreneur Magazine
5.22.2008
Working class 'has lower IQ'?! subject open to debate

The working classes have lower IQs than those from wealthier backgrounds and should not be expected to win places at top universities, an academic has claimed.
Bruce Charlton, reader in evolutionary psychiatry at Newcastle University, suggested that the low numbers of working-class students at elite universities was the "natural outcome" of IQ differences between classes.
In a paper shown to the Times Higher Education magazine, Dr Charlton questioned the Government's drive to get more students from poor backgrounds into top universities like Oxford and Cambridge.
He said: "The UK Government has spent a great deal of time and effort in asserting that universities, especially Oxford and Cambridge, are unfairly excluding people from low social class backgrounds and privileging those from higher social classes.
"Yet in all this debate a simple and vital fact has been missed: higher social classes have a significantly higher average IQ than lower social classes."
The fact that so few students from poor families get into Oxbridge is not down to "prejudice" but "meritocracy", he said.
The Government criticised Dr Charlton's comments. Higher education minister Bill Rammell said: "These arguments have a definite tone of 'people should know their place'.
"There are young people with talent, ability and the potential to benefit from higher education who do not currently do so. That should concern us all."
Sally Hunt, general secretary of the University and College Union, said: "It should come as little surprise that people who enjoy a more privileged upbringing have a better start in life.
4.15.2008
Cartier

 ond necklace created for Yadavindra Singh the Maharaja of Patiala and in 1904 the first practical wristwatch, the "Santos."
ond necklace created for Yadavindra Singh the Maharaja of Patiala and in 1904 the first practical wristwatch, the "Santos."Louis retained responsibility for the Paris branch, moving to the Rue de la Paix, in 1899. He was responsible for some of the company's most celebrated designs, like the mystery clocks[2] (a type of clock with a transparent dial and so named because their works are hidden[3]), fashionable wristwatches and exotic orientalist Art Deco designs, including the colorful "Tutti Frutti" jewels.
Jacques took charge of the London operation and eventually moved to the current address at New Bond Street.
Among the Cartier team was Charles Jacqueau, who joined Louis Cartier in 1909 for his entire life, and Jeanne Toussaint, who was Director of Fine Jewelry from 1933 on.After the death of Pierre in 1964, Jean-Jacques Cartier (Jacques's son), Claude Cartier (Louis's son), and Marionne Claudelle (Pierre's daughter) — who respectively headed the Cartier affiliates in London, New York and Paris — sold the businesses.
In 1972 a group of investors led by Joseph Kanoui bought Cartier Paris. President Robert Hocq, the creator of the concept of "Les Must de Cartier" (a staff member is said to have said "Cartier, It's a must!"[1] meaning something one simply must have) in collaboration with Alain Dominique Perrin, General Director, began introducing new products representative of the status and quality of the Cartier of the past. In 1974 and 1976 respectively, Cartier London and Cartier New York were bought back. In 1979 the Cartier interests were combined together, creating "Cartier Monde" uniting and controlling Cartier Paris, London and New York.
Cartier's largest stores are found in New York, Milan, Beverly Hills, Rome, Boston, San Francisco, Tokyo, Paris, São Paulo, Shanghai, London and Vancouver.
Coco Chanel
 The little black dress, tweed suits, costume jewellery and red lipstick - we owe them all to Gabrielle 'Coco' Chanel. Read more here...
The little black dress, tweed suits, costume jewellery and red lipstick - we owe them all to Gabrielle 'Coco' Chanel. Read more here...The House of Chanel, more commonly known as Chanel, is a Parisian fashion house in France founded by Coco Chanel (b.1883 - d.1971). According to Forbes, the privately held House of Chanel is jointly owned by Alain Wertheimer and Gerard Wertheimer who are the grandchildren of the early (1924) Chanel partner Pierre Wertheimer.

The house of Chanel was founded by Gabrielle Bonheur "Coco" Chanel in 1910. The iconic Chanel logo is one of the most recognizable status symbols in the fashion world with its overlapping double 'C'. The brand began as a small shop which originally sold ladies hats but the boutique quickly gained popularity and within a year moved to the fashionable Rue Cambon district in France. "Coco" and the Parisian fashion house had set out to conquer not only Paris but the rest of the fashion world. Read more here...

LVMH Moët Hennessy • Louis Vuitton

 A world leader in luxury, LVMH Moët Hennessy - Louis Vuitton possesses a unique portfolio of over 60 prestigious brands. The Group is active in five different sectors:
A world leader in luxury, LVMH Moët Hennessy - Louis Vuitton possesses a unique portfolio of over 60 prestigious brands. The Group is active in five different sectors:Wines & Spirits Fashion & Leather Goods Perfumes & Cosmetics Watches & Jewelry Selective retailing
 g young artists and designers.
g young artists and designers.Read more here...
Yves Saint-Laurent

In 2002, dogged by years of poor health, drug abuse, depression, alcoholism, criticisms of YSL designs, Saint-Laurent closed the illustrious couture house of YSL. While the house no longer exists, the brand still survives through its parent company Gucci.
The prêt-à-porter line is still being produced under the direction of Stefano Pilati after Tom Ford left in 2004. His style is decidedly more French than the overtly sexy image that Tom Ford perpetuated.
Christian Dior

Luxury brands
 A luxury brand or prestige brand is a brand for which a majority of its products are luxury goods. It may also include certain brands whose names are associated with luxury, high price, or high quality, though few, if any, of their goods are currently considered luxury goods. The automobile manufacturer Hummer is an example of such a brand, as a Hummer automobile is considered a status symbol, even though none of the vehicles in the Hummer line-up meet the requirements to be classified as a luxury car.
A luxury brand or prestige brand is a brand for which a majority of its products are luxury goods. It may also include certain brands whose names are associated with luxury, high price, or high quality, though few, if any, of their goods are currently considered luxury goods. The automobile manufacturer Hummer is an example of such a brand, as a Hummer automobile is considered a status symbol, even though none of the vehicles in the Hummer line-up meet the requirements to be classified as a luxury car.Another market characteristic of luxury goods is their very high sensitivity to economic upturns and downturns, high profit margins as well as prices, and very tightly controlled brands. Other guidelines may apply to certain luxury markets such as the luxury vehicle market.
For example, following a nearly crippling attempt to widely licence their brand in the 1970s and 1980s, the Gucci brand is now largely sold in directly-owned stores. The Burberry brand is generally considered to have diluted its brand image in the UK in the early 2000s by over-licensing its brand, thus reducing its cachet as a brand whose products were consumed only by the elite.
LVMH (Louis Vuitton Moet Hennessy) is the largest luxury good producer in the world with over fifty brands, including Louis Vuitton, the brand with the world's first designer label. The LVMH group made a profit of €2bn on sales of €12bn in 2003. Other market leaders include PPR (after it purchased the Gucci Group) and Richemont
4.03.2008
2.29.2008
Happiness-centred Business model
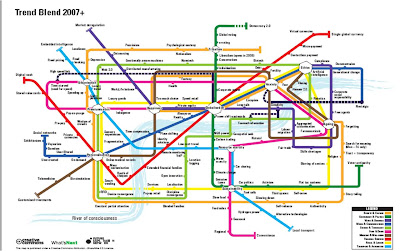
Click here for the full Trend Blend 2007+ map
Future Exploration Network is a company that assists major organizations globally to gain insights into the future and develop strategies that create competitive advantage, along with NowandNext -a trends report company offering clear, concise and non-sensationalist commentary on trends in society, business, science & technology, government and the environment; issues covers new trends, innovations and ideas across twelve sectors and speculates about future risks and opportunities.
These two innovative companies released The trend map 2007 inspired by the subway map of the city of London.The map shows some of the major trends across ten segments: society & culture, government & politics, work & business, media & communications, science & technology, food & drink, medicine & well-being, financial services, retail & leisure, and transport & automotive, as well as the key intersections between the trends. We can see some of the more interesting trends in the landscape. The map deals with ideas (with the River of Consciousness standing in for the Thames).
For a start this map is not meant to be taken too seriously… but still there is some truth in it.
We can see on this map many disruptive trends that are driving new business models.
I have selected one trend that interests me more than others: HAPPINESS.Actually it takes someone to be either brave or a dreamer to even think about tackling this topic. Before I start, let me say that I know there is no ‘logical answer’ or consensus to this concept I don’t think there might exist one universal standard or school of thought when it comes to this topic, perhaps just an ideagoras of different thoughts, ideas and philosophies. Like most of you, I’m still exploring it, which is why I have chosen to make it just that; a discussion and a group exploration.In fact Happiness is an issue which is relevant to every person on the planet. It’s probably the one topic which commands universal interest.
So What is Happiness? and how is it related to business as a trend?
Happiness can mean different things to different people. We might think that happy people have lots of money, are physically attractive, have great jobs, or own the latest gadgets. Or, we might just think happy people are plain lucky, and are born that way. Research suggests, however, that there are a number of variables that make a far greater contribution to happiness than external and more superficial factors.
That doesn't mean that if we have a lot of money we won't be happy, or that having a lot of money is bad, it just means that other factors are more important in determining happiness. In fact, a strong positive relationship between job status/income/wealth and happiness only exists for those who live below the poverty line and/or who are unemployed.
Actually,what distinguishes happy people from the unhappy, is that they have a different attitude in life- a different way of thinking about things and doing things. They interpret the world in a different way, and go about their lives in a different way.
The "Happiness Equation"
It has been suggested that there are several factors that contribute towards our happiness. This is an 'equation for happiness' suggested by Martin Seligman, an American based psychologist:
H = S + C + V
H = Happiness
S = Set range - (genetics: about 50%)
C = Circumstances (8-15%)
V = Voluntary Control - (past, present, future)
If we take a closer look to our daily lives we see that everything is speeding up thanks to our obsession with technology and efficiency - although whether anything is actually moving in the right direction is a moot point. We can blame computers, email, the Internet, globalisation, mobile devices, low cost travel, whatever you like. The result is 24/7 access to goods and services, multi-tasking, meals in minutes, hectic households, microwave mums, meals on the run, insecurity, one minute wins and individuals (and organisations) that want everything tomorrow. The result is a lot of stress, anxiety, chronic lack of sleep, a blurring of boundaries between work and home, work-life imbalance and, conversely, an interest in slowing things down.
So as we see, Happiness seems to be an ever more elusive ideal in society of empty materialism, violence and spiritual crisis. Yet, as we all know the United States Constitution is dedicated to the pursuit of it. Happiness is supposed to be what we are all here to achieve.
Talking about "The pursuit of Happiness"Forbes Magazines published in 1917 an article "The Pursuit of Happiness" explainig that
Business was originated to produce happiness, not to pile up millions. 90 years latter Happiness has not taken a single wrinkle; it is as powerful as ever as a business trend.
How this trend is influencing business models ?
Major businesses are custumer-based models, but I see a shift to this new trend which is going to be hapiness-based model businesses, to explain this in plain words:Customer centered models can have the net effect of creating an imbalance within a business. No one will argue the fact that customers are an important leverage point in any business. However, it is quite another thing to say that the customer is in the center and the world revolves totally around them.
The ultimate lowest common denominator that ties us all together on this planet is our individual desire to seek happiness. At work, happiness is derived from each of us realizing our full potential.
Abraham Maslow defines this as Self-Actualization - the instinctual need of humans to make the most of their abilities and to strive to be the best they can. In order for companies to reach their full potential, they need their team members to reach their individual goal of self actualization first. Only then, through this cummulative effect of the self actualization of the individual team members, can the company acheive the same goal. It follows that if the company is reaching its full potential, it should be maximizing the value for its customers, vendors, stockholders and the community at large as well.
Every business has five stakeholders; customers, team members, stockholders, vendors and the community at large. The only truly sustainable business model that will lead to organizations realizing their full potential is one that focuses on happiness creation as it’s center. Creating happiness for customers for sure, but also and equally important for all of the other stakeholders at the same time.
through my quest online I came accross the book "BUILDING A HAPPINESS CENTRED BUSINESS" which describes how Brisbane, Australia, dentist Dr Paddi Lund turned his dental practice into a happiness centred business, and has lots of lessons for any business, large or small.
You may be wandering, what has happiness got to do with running a business. Well, it has a lot to do with it. Not only whether you enjoy going to your business … but "happiness" in your business reflects on the bottom line.
So you may wander how did he create a "happiness centred business" that is fun, enjoyable, and profitable. Well heripped up his front reception desk with a chainsaw, fired his "C" and "D" clients, built his surgery around a kitchen so you'd smell fresh scones instead of dental smells... and ... now works half the hours and earns triple the income.
Dr Paddi Lund is the self-confessed "Crazy Dentist" from Queensland, Australia. "Crazy" because he's doing so many outrageous things in his practice and because his success defies all conventional business paradigms. He's built a 'By Invitation Only' business that thrives despite the fact that he locked his front door, took down all his signs and removed his name from the phone book! It's hard to believe he's still in business, let alone hugely successful. And successful he is.
Paddi works only 22 hours a week yet makes 3 times more than the majority of his colleagues.
His team never leave, and his customers are clamouring to buy his services.
But more than that, Paddi loves coming to work and has a rich, fulfilling life as a result. All this from focussing on just one aspect of business: not marketing nor advertising, his products, services nor even profits ... but HAPPINESS!!! Business Happiness, to be precise!
It's in fact very rare to find people who... Are massively passionate about what they do,
Are exhilarated by their work, and, Look forward to Monday morning.
While most people think the purpose of business is to create wealth, Dr Paddi Lund takes a different view: if in fact we’re miserable in the process, what's the point of earning the money in the first place?
As far as Paddi's concerned, the real purpose of a business is to add happiness to your life - that without some enjoyment in the process, you just can't keep going with your business for very long, despite the money.
It is to say the least An Unusual Profession ... for a Business Guru! Dentistry is, after all, a universal - in that we all have been to the dentist at some time and most likely have had a bad experience!
Paddi has created one of the most incredible customer service experiences in the world, and let's face it, if he can do it in dentistry, just think what you can do in your profession!
My second example will be about happiness in health and food businesses there are in fact easier and faster ways to put a smile back on your face using what I like to think of as "Happy Food". No, it's not about slipping illegal substances into your brownie recipe, but cooking with ingredients shown to have certain health benefits I supose Gordon Ramsay can best fit in for him Running a retaurant is like baking a cake . It is important to have a balance among three things: Food Cost, Overhead/Staffing and Profits. To much of any of three, and the cake ends up being a horrible mess.
In business, this is much the same. Every business has cost associated with doing the business, a tech business has intellectual property or the idea itself, a services business might have time or media costs, and a product business has manufacturing costs.
Spend too much on physical costs or staffing/overhead you eat up your profits. Spend too much effort on generating profits, and you will lose customers/clients or create opportunity costs.
Baking a cake takes more than just combining a bunch of ingredients and throwing it in the oven. Same could be said for running a business.
Here is a video about his method of running a business not directly suggesting happiness but passion for his job and a great sense of perfection.
and also this video:
How does Ramsay teach people how to run a profitable restaurant? It's not what you may be thinking. He isn't about cutting costs, shoddy work, and cheap labor. Ramsay is all about profit through excellence and skill. That's what attracts people to a restaurant and keeps them coming back...and back. Good food, good service, good atmosphere, happiness and enjoyment in what they are doing.
How Happiness as a disruptive trend inter-reacts with the other trends present on the map?
Happiness as a concept and as a trend is closely related to other factors and trends present on the market and on the map,all trends have interelation and thus affect one another, Globalizaton in itself is a major market disruptor.
Happiness (as station on the map) is almost central to all the Network,it's line includes Anxiety(station) and goes to Personalisation(station) closer stations or spots are as we see it on the map :Too much choice,Health Work/Life balance,Luxury goods and many other disruptive factors.
I defenitly see the future of the Happiness trend as flourishing,expanding and spreading to almost all sorts of businesses mainly leisure health and wellbeing businesses. Happiness-based business model is a real shift which can grow positivly worldwide in unthinkable ways.
2.28.2008
Starwood E-Biz model
Consumer Forum 2004, New York, September 19, 2004, a Forrester Research's event.
2.23.2008
Happiness economics
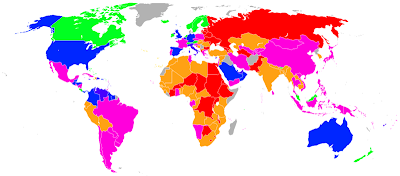
Satisfaction with Life Index Map - Map has no authentic source. Map coloured according to The World Map of Happiness, Adrian White, Analytic Social Psychologist, University of Leicester.
green = happiest
blue
purple
orange
red = least happy
Micro-econometric happiness equations have the standard form: Wit = α + βxit + εit.
In this equation W is the reported well-being of individual i at time t, and x is a vector of known variables, which include socio-demographic and socioeconomic characteristics.
Other quantities have been suggested as making people happier. Money correlates with happiness, however at a diminishing rate with how much that amount of money increases.One study, when corrected for social status, showed no correlation between income and happiness. The amount of spare time people have, as well as their control over how much spare time they have, also correlates with happiness. More generally, there is a significant correlation between feeling in control of one's own life and happiness levels. Losing one's job can be a great source of unhappiness.
Children tend to decrease parental happiness, at least until they leave for college, although in terms of a broader life narrative the opposite may be true.Married people are happier, but it is unclear if this is due to the marriage or if already happy people tend to marry.
Source
2.17.2008
NASA and GOOGLE innovation models

NASA Takes Google on Journey into Space
NASA Ames Research Center, located in the heart of California’s Silicon Valley, and Mountain View-based Google Inc. announced plans to collaborate on a number of technology-focused research-and-development activities that will couple some of Earth’s most powerful technology resources.
NASA and Google have signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) that outlines plans for cooperation on a variety of areas, including large-scale data management, massively distributed computing, bio-info-nano convergence, and encouragement of the entrepreneurial space industry. The MOU also highlights plans for Google to develop up to 1 million square feet within the NASA Research Park at Moffett Field.
“Our planned partnership presents an enormous range of potential benefits to the space program,” said NASA Ames Center Director G. Scott Hubbard. “Just a few examples are new sensors and materials from collaborations on bio-info-nano convergence, improved analysis of engineering problems, as well as Earth, life and space science discoveries from supercomputing and data mining, and bringing entrepreneurs into the space program. While our joint efforts will benefit both organizations, the real winner will be the American public,” he added.
“Google and NASA share a common desire-to bring a universe of information to people around the world,” said Eric Schmidt, Google chief executive officer. “Imagine having a wide selection of images from the Apollo space mission at your fingertips whenever you want it. That's just one small example of how this collaboration could help broaden technology's role in making the world a better place.”
As they say it's always better to hear it from the horse's mouth here is Eric Schmidt he speaks in this video at the NASA 50th Anniversary Lecture Series on January 17, 2008 in Washington, DC.
Google and students
2.16.2008
SUPER MODELS FOR REAL ESTATE BUSINESS MODEL!
2.10.2008
2.09.2008
2.07.2008
InnoCentive Business Model or Cash for answers on the largest scientific online network

1. Brief description of the business InnoCentive as a virtual R&D lab:
InnoCentive is a privately-held company which provides a web-based service to Fortune 500 companies to tap into a global community of more than 125,000 engineers, technologists, scientists, inventors, and entrepreneurs for solving development and innovation challenges.Founded in 2001, InnoCentive connects companies, academic institutions, and non-profit organizations, all hungry for breakthrough innovation, with a global network of more than 125,000 of the world's brightest minds on the world's first Open Innovation Marketplace.InnoCentive, based in Andover, Massachusetts, matches scientists and researchers worldwide with companies that have challenging problems to solve and which have exhausted internal means to find real and valuable solutions.
Here bellow is a very interesting interview with InnoCentive CEO about its Business Model:
Thomas Edison, the quintessential inventor, once said that genius is 1 percent inspiration and 99 percent perspiration. But Ralph Bingham the Founder of InnoCentive thinks it's time to update that equation : "There will always be a lot of perspiration involved," Bingham says, "but should the inspiration be 1 percent, or should we make it 10 percent by opening it up to a diverse net of human beings before you put the perspiration in? I think it's time to turn on the radio."
The idea of lanching InnoCentive goes back to the late 1990s, when pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly wondered if it was getting enough bang for its r&d buck, Rakph Bingham president in research and development for Lilly recalled his student days when his professors of organic chemistry would turn to the graduate students and post-docs in their research group and ask for their help in solving some complicated problem or another. The students would come back with different answers, some of which might prove more useful in resolving the problem, others less so.
The idea of InnoCentive came to him from this experience and practical fact and as a strong advocate of open Innocation he submitted the project to Lilly.
Lilly invested several million dollars in 2001 to launch InnoCentive, implementing Bingham's vision of an online marketplace where companies with questions and scientists with potential answers could find each other.It sounds like a business and intelectual 'dating' website, but realistically it is market place to buy and sell intellectual power.
2. What problems does it solve:
To Understand the way InnoCentive works and which kind if problems does it solve we may first watch the way industry works, where a problem only gets exposed to a handful of minds, things get invented, or problems get solved, based on resource allocation. In other words, who is available, and not necessarily because of who's best qualified to respond to that particular challenge.
But in fact,who's 'best' may not even be knowable as solutions often involve a complex interplay between training, experience and serendipity. Sometimes Short of turning to a few high-priced consultants who may or may not solve the problem, the question to ask is : Is there a way for the company to tap into the vast pool of potential knowledge outside its walls and overcome hitches in development that the company's own researchers had been unable to overcome? Or, even to simply improve the solution speed and productivity?
Thinking about the way scientific creativity manifests, it's not always given that the next problem busineses encounter will be solved by a Nobel laureate. Perhaps it will be by some guy at a rural, private college in Mexico or a small research facility in China or a Deutch startup.
So, if there is enough diversity of exposure, would we get new solutions to given problems? the answer is yes.
Bingham has likened his concept to talk radio: If he broadcast an obscure question to millions of listeners, someone out there was likely to call in with the correct answer.
InnoCentive as a platform of open innovation is Changing the world. For example InnoCentive Solvers develops solution to help clean up remaining oil from the 1989 Exxon Valdez disaster. "Green" groups taking advantage of prize-based Innovation to help solve long-term environmental problems: please Check out the InnoCentive Oil Spill Cleanup video , and this is the solver John Davis talking about his innovation and solution to the problem, he won $20,000 for solving the Open Innovation Challenge posted by the Oil Spill Recovery Institute.
In fact, what InnoCentive provides is a "spot" market where companies can get a problem worked on immediately. where companies and innovators can buy and sell intellectual power without the costs associated with facilities, recruiting, career management, negotiations, custom contracting, etc."
Bingham compares this Business model to bounty hunting. While companies have spent more than a million dollars on challenges they've solved through InnoCentive, that's much less than it would have cost to invest in internal r&d to resolve them. Most importantly, they've paid ONLY for solutions and not for attempted solutions in the risky venture of R&D.
Innocentive, provides an exchange where “seekers’’ can offer cash to “solvers’’. Both sides are anonymous, which is one of the selling points of innovation prizes: they reward neither connections nor seniority, but solutions alone.
Personally I find Innocentive’s problems ads rather funny because they read a little like the small ads on the world’s least romantic lonely-hearts website: for example “A technology is desired that produces a pleasant scent upon stretching of an elastomer film’’ ($50,000). “Surface chemistry for optical biosensor with high binding capacity and specificity is required’’ ($60,000).
a. For InnoCentive Customers
In order to achieve and maintain competitive leadership and create breakthrough discoveries, corporations and non-profits face the challenge of continually seeking out new ideas and solutions. So,by signing up as a Seeker organization, these progressive companies can supplement internal R&D and Product Development resources by reaching out to some of the world's most creative thinkers; people who thrive on solving tough challenges.
There is about 40 'seeker' companies which have signed up with InnoContive, posting challenges in a wide range of scientific disciplines, including the fields of chemistry and applied sciences—such as material and polymer sciences—and the life sciences, and offering rewards ranging from $10,000 to $125,000 for working solutions. Now, over 40 blue chip companies, from Boeing to Dow Chemical, DuPont, Lilly, Novartis, and Procter & Gamble are among the seekers and thy post problems with InnoCentive.
Still, many companies are reluctant to turn to outsiders like the InnoCentive Open Innovation platform for help with products in the pipeline. Fundamentally, most places still run the old, classic, 'my lab, my walls' system, so there is a huge market oportunity for Innocentive in the future.
b. InnoCentive Suppliers
Nearly 135,000 'Solvers' from some 175 countries have registered on the InnoCentive website, where they can find new challenges each week. Tens of thousands of solvers might read the abstract of a challenge, but only a few hundred who think they can realistically solve it continue to the details.
c. Innocentive Partners
The company has partnered with 59 research institutions and scientific organizations in Russia (35), China (20), and India (4) to access more scientists.
The Rockefeller-InnoCentive Partnership enableS researchers and entrepreneurs addressing the needs of poor or vulnerable people to access the same cutting-edge resource to innovate as Fortune 500 companies.The Rockefeller Foundation-InnoCentive partnership brings the benefits of this model to those working on innovation challenges faced by poor or vulnerable people. The Rockefeller Foundation will pay access, posting and service fees on behalf of these new class of “seekers” to InnoCentive, as well as funding the awards to "problem solvers."
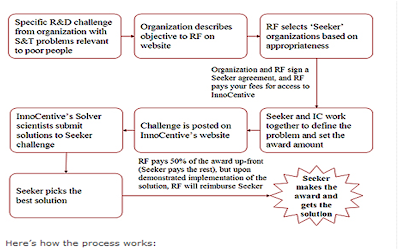
I see this as what we call Teaching an old dog new tricks.For an organisation that has suffered from “not invented here” syndrome, Rockefeller by teaming up with InnoCentive, the online business that posts problems and offers rewards to innovators who solve them. Rockefeller will provide funding to adapt this “open innovation” model to helping the poor. Next are likely to be projects on climate change and on the growing economic insecurity that many people experience. Whether all of this will accomplish remains to be seen.
d. InnoCentive Owner:
As an open Innovation strong advocate Alpheus Bingham is the Co-Founder of InnoCentive he is himself an innovator by launching this succesful and original website which he runs with InnoCetive management team .
InnoCentive's President and CEO, Alpheus Bingham, was a senior research executive at Eli Lilly and has over 28 years experience as a scientist, and its Chief Marketing Officer and VP of Global Markets, Ali Hussein, is a leading expert in Chinese, Indian and Russian scientific communities, and was Director of Marketing and Business Development for Amazon.com's wireless initiative, Amazon Anywhere. So this is a company where R&D expertise meets the ultimate in internet know-how.
3. Innocentive customer groups
In the past, R&D departments worked more or less on their own, while today the so-called Open Innovation concept is becoming increasingly widespread Companies are thus able to cost- effectively "outsource" highly specialized tasks to a large pool of inventors around the world when they lack the in-house expertise.Innocentive's site, which is essentially a marketplace for inventors, has expanded considerably since pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly started it in 2001. Now even some of Lilly's competitors use the site, including BASF, Novartis, Nestlé and Procter & Gamble, which has increased the share of product ideas accepted from outside inventors from 20 to 35 percent over the last three years.
Of the 350 challenges posted on InnoCentive since it opened, about a third have been solved. The average posted reward is about $30,000; the highest awarded amounts to date have been three awards at $75,000 each (though higher bounties have been offered.) In return, scientists who present solutions sign over the intellectual property rights.
4. InnoCentive revenue sources
From the “seeker,” InnoCentive collects posting fees for the use of its platform. In addition, depending on the type of challenge, InnoCentive receives a commission on awards made by the “seeker” to the “problem solver.” So, for a relatively modest fee and comparatively minor effort , “seekers” significantly increase their research capacity.practically speaking at InnoCentive, companies pay an annual $80,000 access fee to post problems anonymously on the website. They also pay the rewards for the best solutions and a commission of 20% or more to InnoCentive.
5. InnoCentive main competitors
InnoCentive's growth has mirrored a developing trend in open innovation and external collaboration, a trend that has also spawned competitors such as NineSigma which enables clients to source innovative ideas, technologies, products and services from outside their organizations quickly and inexpensively by connecting them to the best innovators and solution providers from around the world. Its unique "Discover-Connect-Solve" approach is based upon the principles of Open Innovation. Their clients access one of the the largest and most comprehensive open network of scientific researchers in the world to solve their business needs.
- another 'competitor' is :status quo.
- an other example of these companies is Netflix, a film rental website which offers recommendations based on what you looked at, bought, rented or reviewed in previous visits,Netflix has skipped middlemen like Innocentive. In March 2006, the chief executive of Netflix, Reed Hastings, met some colleagues to discuss how they might improve the recommendation system, Cinematch. Hastings, inspired by the story of John Harrison, suggested offering a prize of $1m to anyone who could do better.
The Netflix prize, announced in October 2006, struck a chord with the Web 2.0 generation. Within days of the prize announcement, some of the best minds in the relevant fields of computer science were on the case. Within a year, the leading entries had reduced Cinematch’s recommendation errors by more than 8 per cent – close to the million-dollar hurdle of 10 per cent. And it has cost Netflix very little to mobilise all this effort. The company has had to pay out a mere $50,000 progress award, to a team of three AT&T data analysts.Even Netflix is surprised at how well it’s been going. “We just didn’t think the relevant research community was so big,’’ says Steve Swasey, vice-president. Source
6. Can the model apply offline as well, or it is unique to the web? I think that as a virtual R&D LAB and being the largest scientific online network the model can not apply offline because its success is closely related to the development of the Web 2.0 generation, as a virtual laboratory,InnoCentive has developed a unique virtual platform reducing both the time and the risks providing solutions faster then any offline R&D platform and community.
7. Scalability and sustainability of InnoCentive Business Model
InnoCentive capitalized on the fact that major companies spend billions of dollars on research and development that could more effectively be outsourced. What if a company had not just a handful of problem solvers, but a worldwide network of problem solvers all working on their hardest nuts-to-crack, and at a fraction of the typical R&D cost? In what it terms as a “virtual laboratory,” the company’s website, is accessed by over 90,000 scientists and scientific organizations located in over 175countries (and like everything on the worldwide web, this number continues to organically grow).
it is sustainable beccause it is a very innovativ e-business operation. Lilly's idea was to use the "power of the Internet" to enhance scientific collaboration. The Internet offers an unparalleled means of exchanging information and connecting people. InnoCentive has taken advantage of this, logging thousands of miles, literally and electronically, to build its network.
Fast Company’s Most Innovative Business People of 2007
8. Stretching of the idea:
What first caught my eye in this business model analysis is InnoCentive's novelty. I love when a company makes me say, “Why didn’t I think of that?!"). Its business model is one that comes directly out of our new, modernized world. We live in a world full of smart people out there, and now with the internet, we have the ability to reach them. Why should companies limit their brainpower to those found on their individual payrolls?
a. How to increase InnoCentive users or customers:
This business is expanding in leaps and bounds internationally, but in order to reach more customers it has to be launched in many languages and open the platform to new feilds of research and innovation.
b. We can Expand revenue sources – not just increase revenue from existing sources by:
- opening the platform to new disciplines such as law and finance and also publishing.
- In an ideal world :opening the platform for "solvers" to submit new innovative concepts and ideas and connect them with companies and investors who may be interested to make them real.peôple may have innovative ideas to problems that companies havent encountered yet, so it will be a sort of anticipation process.





